AAS Spectrometer: A Precision Tool for Metal Detection in Analytical Chemistry
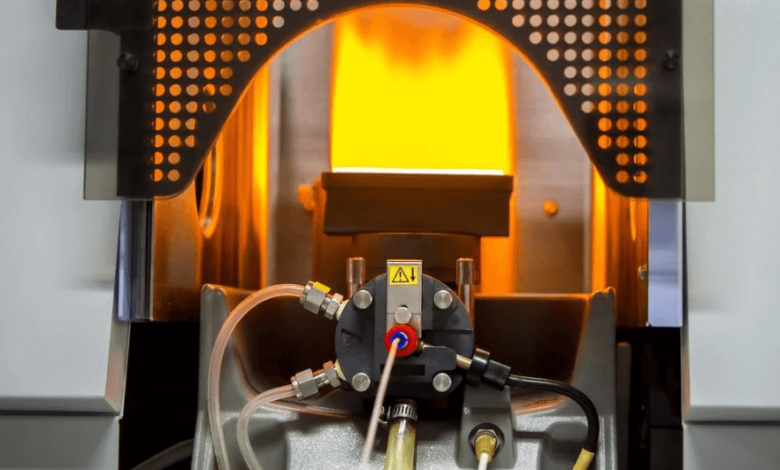
In today’s fast-paced scientific world, the demand for accurate, cost-effective, and efficient elemental analysis tools has never been higher. Among the many instruments available, the aas spectrometer remains a trusted choice in laboratories worldwide. Known for its simplicity, reliability, and precision, this instrument continues to serve as a cornerstone in fields such as environmental science, healthcare, metallurgy, food testing, and academic research.
In this article, we delve into the essentials of the aas spectrometer—what it is, how it works, its advantages, primary applications, and the reasons it maintains its relevance despite emerging technologies.
What is an AAS Spectrometer?
The aas spectrometer is an analytical device used to determine the concentration of specific metal elements in liquid samples. AAS stands for Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. This technique is based on the principle that ground-state atoms absorb light at specific wavelengths. Each metal element has a unique wavelength where it absorbs light, allowing for highly accurate and selective measurement.
A hallmark of the AAS spectrometer is its ability to analyze one element at a time with minimal interference, offering precise results even in complex sample matrices. Whether measuring trace lead in drinking water or calcium in food products, this instrument delivers dependable outcomes.
How Does the AAS Spectrometer Work?
The process of measurement using an aas spectrometer follows a clear and well-established workflow. Here’s how it operates:
- Sample Introduction: The sample, typically in a liquid form, is introduced into the system.
- Atomization: The sample is transformed into free atoms by heating—commonly in a flame (Flame AAS) or an electrically heated graphite furnace (Graphite Furnace AAS).
- Light Source: A hollow cathode lamp specific to the element being analyzed emits light at the target wavelength.
- Absorption: As the light passes through the atomized sample, specific atoms absorb the light energy.
- Detection: The amount of light absorbed is measured by a detector, usually a photomultiplier tube.
- Analysis: The absorbed light is directly related to the concentration of the element, and software processes the data to display results.
This precise mechanism allows laboratories to detect metals down to parts-per-billion (ppb) levels with high confidence.
See also: Leveraging Technology to Boost Business Efficiency
Key Features of the AAS Spectrometer
Modern aas spectrometers are equipped with a range of advanced features that make them ideal for both routine and high-sensitivity applications:
- Element-Specific Lamps: High selectivity using hollow cathode lamps tailored to individual metals.
- High Sensitivity: Especially when using graphite furnaces, capable of detecting trace concentrations.
- User-Friendly Software: Most systems now come with intuitive software interfaces, enabling quick calibration, analysis, and data export.
- Compact Designs: Many benchtop models save space without compromising functionality.
- Automation Compatibility: Integration with autosamplers and quality control systems enhances throughput.
Applications of the AAS Spectrometer
The versatility of the aas spectrometer makes it suitable for a wide variety of applications:
🌍 Environmental Testing
- Analysis of heavy metals like lead, arsenic, and mercury in water, soil, and industrial waste.
- Ensures compliance with environmental regulations set by EPA, WHO, and other organizations.
🧪 Pharmaceutical Industry
- Measurement of trace metal impurities in drugs and raw ingredients.
- Conforms to ICH Q3D guidelines on elemental impurities.
🥫 Food and Beverage Quality Control
- Analysis of nutritional elements such as iron, calcium, and magnesium.
- Detection of toxic metals to ensure food safety compliance.
⛏️ Mining and Metallurgy
- Quantification of metal content in ores and alloys.
- Assists in quality control and metal recovery processes.
🌾 Agriculture and Soil Science
- Assessment of micronutrients and harmful metals in fertilizers, crops, and soil.
- Aids in improving agricultural productivity and safety.
Flame AAS vs. Graphite Furnace AAS
Depending on the required sensitivity and sample type, an aas spectrometer typically comes with one of two atomization technologies:
🔥 Flame AAS
- Atomization via an air-acetylene or nitrous oxide-acetylene flame.
- Suitable for ppm-level detection.
- Preferred for high-throughput and less sensitive applications.
⚫ Graphite Furnace AAS
- Uses an electrically heated graphite tube to atomize samples.
- Ideal for ppb-level detection and low-volume samples.
- Used in high-precision applications like clinical testing and pharmaceutical analysis.
Some aas spectrometer systems are hybrid, offering both methods for maximum flexibility.
Benefits of Using an AAS Spectrometer
There are several reasons why the aas spectrometer continues to thrive, even as newer technologies like ICP-MS and ICP-OES gain popularity:
✅ Cost-Effective
Lower capital and operating costs compared to multi-element instruments make it accessible for small to medium-sized labs.
✅ Simple to Use
The operation, calibration, and maintenance of an aas spectrometer are relatively straightforward, reducing training time and error rates.
✅ Accurate and Reliable
The single-element focus reduces spectral interferences, enhancing data quality and repeatability.
✅ Low Sample Volume Requirement
Especially with graphite furnace AAS, very small sample sizes can yield high-quality results—ideal for precious or limited materials.
Choosing the Right AAS Spectrometer
When selecting an aas spectrometer, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Type of Analysis: Determine whether you need high-throughput or trace-level sensitivity.
- Elemental Range: Ensure the instrument supports your specific metal targets with the appropriate lamps.
- Automation Needs: For busy labs, autosamplers and barcode integration can significantly improve productivity.
- Software Features: Look for built-in quality control features, data export formats, and user management.
- Support and Service: Choose vendors that offer strong technical support, training, and local servicing.
Popular manufacturers include Agilent Technologies, PerkinElmer, Analytik Jena, Shimadzu, and Drawell.
Maintenance Tips for AAS Spectrometer Longevity
To ensure consistent performance from your aas spectrometer, follow these best practices:
- Routine Calibration: Use certified reference materials for frequent verification.
- Clean Burners and Furnaces: Prevent residue buildup that can affect accuracy.
- Check Gas Supply: Maintain stable flame operation with proper gas pressure.
- Lamp Replacement: Change hollow cathode lamps as per manufacturer’s lifespan guidelines.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your system’s firmware and analysis software current.
Future Innovations in AAS Technology
Although the basic principle behind the aas spectrometer has remained consistent for decades, modern versions are incorporating smart features such as:
- Remote Operation: Wi-Fi and cloud connectivity for remote control and monitoring.
- AI Diagnostics: Predictive maintenance features that warn of upcoming failures.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Reduced gas consumption and energy-efficient atomizers.
- Integrated Compliance Tools: Built-in auditing, data integrity, and report-generation tools.
These advancements ensure that the aas spectrometer remains competitive and compatible with modern laboratory workflows.
Conclusion
The aas spectrometer stands as a testament to effective scientific design—simple in principle, yet powerful in execution. Its focused, accurate analysis of individual metals makes it an indispensable tool in labs across the globe. While more complex instruments exist, the aas spectrometer continues to offer unmatched value where single-element analysis, affordability, and reliability are paramount.
Whether you’re part of a regulatory lab, a manufacturing facility, or a research institute, investing in a robust aas spectrometer can be a game-changer in achieving consistent and reliable elemental analysis.






